ESIM is not widely used due to limited device compatibility and lack of awareness among consumers. Traditional SIM cards still dominate the market.
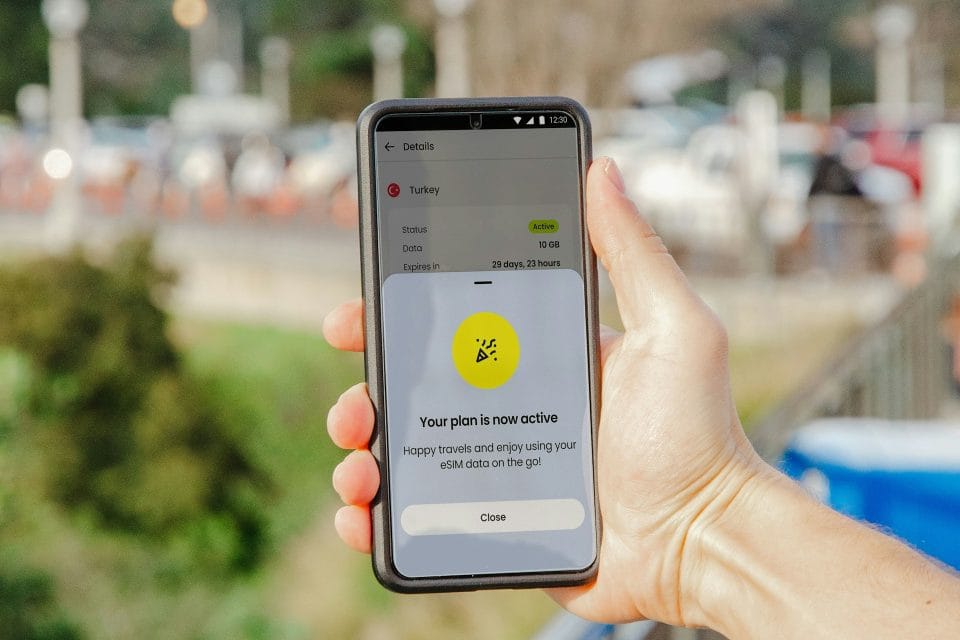
ESIM technology offers a more convenient way to manage mobile connectivity. It eliminates the need for physical SIM cards and allows users to switch carriers easily. Despite these benefits, eSIM adoption remains slow. Most smartphones and devices still rely on traditional SIM cards.
Consumers are often unaware of eSIM capabilities. Carriers also hesitate to promote eSIMs due to existing infrastructures. Overcoming these barriers requires education and support from both manufacturers and service providers. As awareness grows and more devices become compatible, eSIM usage will likely increase. For now, traditional SIM cards continue to hold their ground.

Introduction To eSIM
eSIM stands for embedded SIM. It is a small chip inside your device. Unlike traditional SIM cards, eSIMs do not need to be removed or inserted. This new technology offers many benefits.
eSIM Basics
An eSIM is a digital SIM. It allows you to activate a cellular plan without using a physical SIM card. eSIMs are built into the device. They are rewritable, meaning you can switch carriers easily.
Here are some key features of eSIMs:
- No physical card needed
- Easily switch between carriers
- Less space in the device
- More secure
Current Adoption Rates
Despite its benefits, eSIM usage is still low. Many carriers and devices do not support eSIM. A table below shows current adoption rates:
| Country | eSIM Adoption Rate |
|---|---|
| USA | 30% |
| UK | 25% |
| Germany | 20% |
| India | 10% |
The adoption rates are low due to several reasons. Many carriers are slow to adopt this new technology. Some devices are not compatible with eSIM. People are also hesitant to change from traditional SIM cards.
Technical Challenges
eSIM technology offers numerous benefits, but it faces several technical challenges. These challenges hinder its widespread adoption. The issues range from compatibility to device integration. Let’s explore these technical hurdles in detail.
Compatibility Issues
eSIM technology is not yet compatible with all devices. Many older devices do not support eSIM. This limits the user’s ability to switch to eSIM. Mobile carriers also face compatibility issues. They need to update their systems to support eSIM. This involves significant investment and effort.
Additionally, users may face regional compatibility issues. eSIM standards vary across different countries. This makes international travel more complicated. Users may need to switch to physical SIMs when traveling abroad.
Integration With Devices
Integrating eSIM into existing devices is complex. Manufacturers need to redesign hardware to support eSIM. This adds to the development time and cost. Not all manufacturers are ready for this change.
Furthermore, integrating eSIM requires new software. Devices need updated firmware to handle eSIM. This is an additional challenge for manufacturers. They need to ensure their software is secure and reliable.
Here are some key integration challenges:
- Redesigning device hardware
- Updating device firmware
- Ensuring software security
- Maintaining reliability
These technical challenges slow down eSIM adoption. Overcoming them requires time, investment, and collaboration. Until then, eSIM will not be widely used.
User/Consumer Concerns
Consumers have several concerns about eSIM technology. These concerns slow down its widespread adoption. This section explores these concerns in detail.
Awareness Levels
Awareness about eSIM is still low among most consumers. Many people don’t know what eSIM is or how it works. This lack of knowledge creates hesitation. People stick with traditional SIM cards because they are familiar.
Schools and tech blogs need to educate more about eSIM. Education can help increase awareness levels. Higher awareness will lead to higher adoption rates.
Perceived Benefits Vs. Costs
Consumers often weigh the perceived benefits of eSIM against its costs. They look at the advantages, like not needing a physical SIM card. But, they also consider potential costs.
Here is a table that summarizes perceived benefits and costs:
| Benefits | Costs |
|---|---|
| No physical SIM card needed | Possible higher initial cost |
| Easy to switch carriers | Compatibility issues |
| Supports multiple profiles | Fear of hacking |
Consumers see the benefits but worry about costs and security. These worries slow down the adoption of eSIM technology.
Industry Resistance
The adoption of eSIM technology faces significant hurdles. One major challenge is industry resistance. Many players in the telecom industry hesitate to fully embrace this innovation. Let’s explore the reasons behind this resistance.
Telecom Provider Hesitations
Telecom providers show reluctance towards eSIM technology. This is due to several concerns:
- Customer Control: eSIMs give users more control over switching networks. This reduces provider control.
- Infrastructure Costs: Providers need to invest in new infrastructure. This incurs additional costs.
- Security Issues: There are worries about potential security risks. These could affect both users and providers.
Market Dynamics
Market dynamics also play a role in the slow adoption of eSIMs. Some factors include:
- Device Compatibility: Not all devices support eSIM technology. This limits its widespread use.
- Consumer Awareness: Many consumers are unaware of eSIM benefits. This slows down adoption rates.
- Market Competition: Traditional SIM cards still dominate the market. This creates competition for eSIM technology.
Future Outlook
The future of eSIM technology holds immense potential. Despite current adoption challenges, advancements are paving the way for wider usage. This section explores the future outlook of eSIM by focusing on its growth potential and technological advancements.
Potential For Growth
eSIM technology is growing at a rapid pace. More devices are expected to support eSIM in the near future. This includes smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices. The flexibility of eSIM attracts many users. They can switch carriers without changing physical SIM cards. This is particularly useful for frequent travelers.
In the business world, eSIM can simplify fleet management. Companies can manage multiple devices without handling physical SIM cards. This reduces logistical complexities. It also minimizes the risk of losing or damaging SIM cards.
As 5G networks expand, the demand for eSIM will grow. 5G offers faster speeds and more reliable connections. eSIM can enhance these benefits by providing seamless network switching. This ensures users always have the best connection available.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are crucial for eSIM adoption. Enhanced security features are being developed. These features protect user data and privacy. This is vital in an age where data breaches are common.
eSIM profiles can be downloaded over the air. This eliminates the need for physical SIM cards. Users can activate their devices instantly. This is convenient and saves time.
Manufacturers are designing devices with eSIM compatibility. This includes major smartphone brands. With more eSIM-enabled devices, users have more choices. This drives the adoption of eSIM further.
Additionally, eSIM technology is evolving to support multiple profiles. Users can have multiple carrier profiles on a single eSIM. This is beneficial for those who travel frequently or have multiple mobile plans.
In summary, the future outlook of eSIM is promising. Growth potential and technological advancements are key drivers. The adoption of eSIM is expected to increase, making it a mainstream technology.

Frequently Asked Questions
Why Isn’t EeSIM Popular Yet?
ESIM adoption faces challenges due to limited device support, carrier restrictions, and consumer unfamiliarity.
What Are The Barriers To eSIM Usage?
Barriers include lack of widespread support from carriers, limited device compatibility, and consumer awareness.
How Does eSIM Affect Phone Flexibility?
ESIM enhances phone flexibility by allowing easy switching between carriers without physical SIM cards.
Is eSIM Technology Secure?
Yes, eSIM technology is secure. It uses robust encryption standards for data protection.
Conclusion
The limited adoption of eSIM technology stems from compatibility issues and privacy concerns. Lack of widespread carrier support also plays a role. As technology evolves, eSIM adoption may increase. Consumers need more information and assurance. Future advancements could overcome current obstacles, leading to broader acceptance and use of eSIMs.