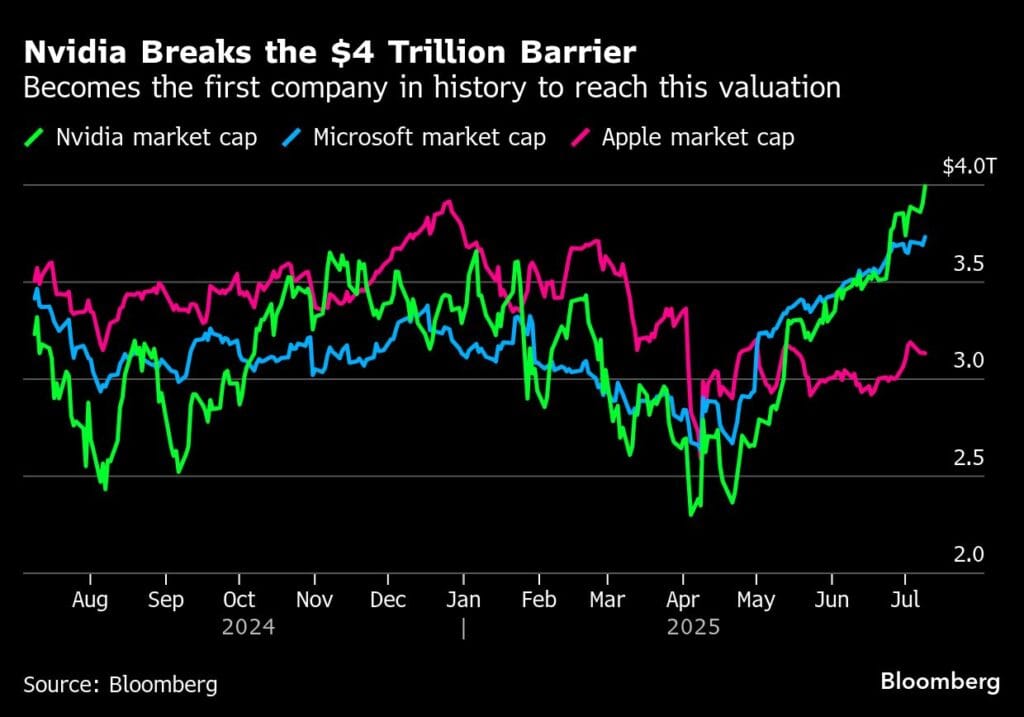
Nvidia has just made tech history. In 2025, it became the first-ever $4 trillion company. On July 9, 2025, Nvidia, a company that makes computer chips, became the first publicly traded company to reach a $4 trillion market value. This means the total value of all its shares was over $4 trillion for a short time during trading. By the end of the day, its market cap was $3.97 trillion, still higher than any other company. This milestone shows how important Nvidia has become in the tech world, especially in artificial intelligence (AI).
This is a very big deal in the world of business and technology. Many people around the world are now talking about Nvidia. But what does this really mean? Why is it so important? And how did Nvidia become so valuable?
Let’s explore how Nvidia Touches Unprecedented $4 Trillion Valuation
What Is NVIDIA?
Nvidia is a big technology company from the United States. It is best known for making graphic cards, also called GPUs (Graphics Processing Units). These are powerful chips that help computers show pictures, games, and videos.
But now, Nvidia is not just about games. It is also helping in artificial intelligence (AI), data centers, robotics, cars, and more. This helped Nvidia grow very fast.
Nvidia’s $4 trillion valuation is a big deal. It shows that AI is changing the world and creating huge value. Nvidia’s chips power AI systems used by companies like OpenAI, which made ChatGPT. As more businesses use AI, Nvidia’s products are in high demand. This achievement also puts Nvidia ahead of tech giants like Apple and Microsoft, which were worth about $3.1 trillion and $3.3 trillion, respectively.
What Drives Nvidia’s Success? The $4 Trillion Milestone
Nvidia’s growth comes from its leadership in making graphics processing units (GPUs). These chips are great for AI because they can handle complex math quickly. The boom in generative AI, which creates things like text, images, or music, has boosted Nvidia’s sales. In May 2025, Nvidia reported a profit of $18.8 billion and revenue of $26 billion, up 262% from the previous year. Their data center business, which supports AI, grew by 427%.
Why Did Nvidia Grow So Fast?
There are many reasons. Let’s look at the top ones:
1. Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is now part of everything – from chatbots to self-driving cars. AI needs very strong chips to work. Nvidia makes the best chips for AI. These chips are called H100, A100, and the newer B100.
2. Boom in Data Centers
Big companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon use Nvidia chips in their data centers. These places have lots of computers running 24/7. They need powerful GPUs, and Nvidia is the first choice.
3. Demand in Gaming & Graphics
Even though AI is big, gaming is still strong. Many people use Nvidia GPUs in their computers and gaming consoles. New games need better graphics, and Nvidia is always ahead.
4. Smart Cars & Robotics
Nvidia also makes chips for self-driving cars and robots. Companies like Tesla and Toyota use Nvidia’s technology to train AI for driving.
Stock Price Explosion
In just a few years, Nvidia’s stock price went up many times. In 2020, Nvidia stock was under $100. By mid-2025, it had gone over $1,000 per share. This made many investors rich.
Even small investors who bought early saw huge profits. Big investors like BlackRock and Vanguard also earned billions from Nvidia shares.
Products That Made Nvidia Billions
Let’s look at some popular Nvidia products:
- RTX 4090 & 4080: For high-end gaming
- H100 Tensor Core: For deep learning and AI training
- Jetson Nano: For robotics and edge computing
- Omniverse: A digital platform for building virtual worlds
These products help Nvidia earn billions of dollars every quarter.
Global Reach
Nvidia is used everywhere in the world. Its customers are:
- Tech giants (like Microsoft, Meta, Google)
- Game developers
- Schools and universities
- Military and defense projects
- Crypto mining farms
It has offices and partners in over 50 countries.
Jensen Huang: The Man Behind Nvidia’s Success
Jensen Huang is the CEO and co-founder of Nvidia. He is one of the most respected tech leaders today.
He always believed that GPUs could do more than just run video games. Under his leadership:
- Nvidia expanded into AI, healthcare, automotive, and data centers
- It kept innovating faster than its competitors
- It built software ecosystems like CUDA and Omniverse
Huang is known for his black leather jacket, bold ideas, and focus on the future. Many call him the “Steve Jobs of AI.”
A Quick Look at Nvidia’s History: The Rise of Nvidia
Nvidia was founded in April 1993 by Jensen Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem in Santa Clara, California. Initially focused on creating GPUs for video games, Nvidia’s chips made games look more realistic. In 1997, the company launched the RIVA series, entering the gaming market. In 1998, the RIVA TNT chip boosted its reputation for high-performance graphics. By 1999, Nvidia went public with its initial public offering (IPO) and released the GeForce 256, the first GPU with onboard transformation and lighting (T&L), allowing for more complex graphics without relying heavily on the computer’s main processor.
Nvidia’s success in gaming led to partnerships with major companies. In 1999, it secured a $200 million deal with Microsoft to develop Xbox hardware. In the early 2000s, Sony chose Nvidia to supply the RSX Reality Synthesizer for the PlayStation 3. Beyond gaming, Nvidia worked with NASA in 2003 on a Mars simulation and supplied graphics chips for Audi vehicles, showing its versatility.
The Gaming Revolution
In the late 1990s, Nvidia changed the gaming industry with its GeForce series. Gamers loved the smooth graphics. Soon, almost every gaming PC had a GeForce GPU.
By the early 2000s, Nvidia became a leader in PC graphics cards. It made gaming faster, smoother, and more real-looking. But Nvidia didn’t stop there.
Turning Point: CUDA and AI
In 2006, Nvidia launched CUDA – a tool that allowed its GPUs to work not just for graphics, but for mathematical and scientific tasks. This was a game changer. CUDA turned Nvidia GPUs into mini supercomputers.
AI researchers discovered that Nvidia chips could train machine learning models faster than traditional CPUs. That’s how Nvidia went from just “graphics” to powering the AI revolution.
Nvidia Overtakes Tech Titans (2025 Update)
Nvidia’s $4 trillion milestone underscores AI’s growing role in the global economy. As industries like healthcare, transportation, and entertainment adopt AI, Nvidia’s chips will remain in demand. However, the company must navigate ethical issues, such as AI’s impact on jobs and data privacy. Maintaining its innovative culture will be key as competition and regulations intensify.
| Key Financial Metrics | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Cap (July 9, 2025) | $4 trillion (intraday), $3.97 trillion (close) |
| Stock Price (Close) | $162.88 |
| Q1 2026 Profit | $18.8 billion |
| Q1 2026 Revenue | $26 billion (262% year-over-year growth) |
| Data Center Growth | 427% year-over-year |
| Predicted Stock Price | $196 (within next year, per CFRA) |
| Predicted Market Cap | $4.8 trillion (if stock reaches $196) |
How Nvidia’s AI Chips Are Changing Daily Life?
Today, Nvidia’s GPUs are not just for gamers or data scientists. They are changing real life in many ways. You may not see it directly, but AI services you use daily depend on Nvidia chips.
Chatbots and Voice Assistants
When you talk to tools like ChatGPT, Google Assistant, or Siri, those platforms are trained using Nvidia’s H100 and A100 chips. These chips process huge amounts of data quickly. Without this speed, modern chatbots wouldn’t work as fast or as smart.
Smart Shopping and Recommendations
When you shop online, the platform suggests products based on your interests. That’s AI at work, powered by data centers using Nvidia GPUs. Amazon, Netflix, and YouTube use Nvidia tech to recommend what you watch or buy next.
Self-Driving and Smart Cars
Cars from Tesla and other brands use Nvidia’s DRIVE platform. It helps cars see roads, signs, and people, then make decisions in real time. Nvidia chips are like the car’s brain, helping it move safely.
Medical Research and Health AI
In hospitals and labs, Nvidia GPUs power tools that help detect diseases like cancer or heart problems. AI systems can look at scans and give faster results than human doctors in some cases. These tools can save lives.
Risks and Challenges Nvidia May Face
Even though Nvidia is winning now, the road ahead is not easy. The tech industry changes fast. Let’s look at some challenges Nvidia could face.
High Prices of GPUs
Nvidia’s top GPUs are very expensive. Some AI chips cost over $30,000 each. Smaller companies and researchers can’t afford them easily. This could slow down adoption in some markets.
Chip Shortage and Supply Chain Issues
Global chip supply is still not stable. In the past, Nvidia had to delay shipments. Any new global issue—like war, factory shutdowns, or politics—can hurt Nvidia’s ability to meet demand.
Strong Competition
Companies like AMD, Intel, and new startups like Cerebras and Graphcore are building AI chips. If one of them makes cheaper or better chips, Nvidia could lose customers.
Also, big tech companies like Google and Amazon are making their own AI chips. These are called TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) and Inferentia. If these improve quickly, they might replace Nvidia’s chips in some areas.
Government Rules and Export Bans
Some countries want to stop advanced AI chips from going to other nations. The U.S. already banned Nvidia from selling top chips to China. This reduces Nvidia’s revenue and may create political risks.
Why Investors Still Trust Nvidia?
Even with risks, many investors believe Nvidia will keep growing. Here’s why:
Strong AI Demand
AI is not slowing down. In fact, it’s just beginning. Many sectors like education, security, agriculture, retail, and energy are starting to use AI. This means Nvidia GPUs will stay in high demand for many years.
Market Leader Position
Nvidia holds over 80% of the AI GPU market. Even if new companies enter the race, Nvidia still has the best technology and brand trust.
Software Ecosystem
Nvidia is not just about hardware. It also offers powerful software like CUDA, cuDNN, and TensorRT. These tools help developers build faster and better AI models. Competitors don’t offer such a complete package.
What’s Next for Nvidia?
Nvidia is not stopping. In 2025 and beyond, it plans to enter more sectors and release more powerful chips.
New AI Chips: B100 and Beyond
The new B100 chip is said to be twice as powerful as H100. It also uses less power. This helps companies save money and energy while training large AI models.
Expansion into Edge AI and IoT
Nvidia wants to bring AI to small devices. It already has Jetson boards used in robots, drones, and cameras. In the future, your fridge, phone, or washing machine could use Nvidia AI.
Metaverse and Omniverse
Nvidia is working on the Omniverse—a platform for building virtual worlds and digital twins. Companies can use this to test machines, factories, or cities in 3D before building them in real life.
This will open up new markets, including education, construction, and even the movie industry.
Expanding Into New Territories
Nvidia has started building partnerships in:
- India, for AI in agriculture and education
- Africa, to help build internet infrastructure using edge AI
- Europe, for energy-efficient data centers and climate research
AI Research & Quantum Computing
Nvidia is also investing in AI research labs and quantum computing. It wants to stay ahead of the curve for the next 10–20 years.
AI for Everyone
With cheaper GPUs like the RTX 4060 and Jetson Orin Nano, Nvidia wants to make AI tools available to students, developers, and creators worldwide.
Final Thoughts: A $4 Trillion Giant with a Bigger Future
Nvidia’s journey from a graphics card maker to a $4 trillion AI giant is truly inspiring. It shows how one company can change the world—not just for gamers, but for everyone.
Whether it’s powering your favorite app, helping doctors save lives, or building the future of self-driving cars, Nvidia is at the center of it all.
And the best part? This might only be the beginning.
Frequently Asked Questions
How did Nvidia become the world’s first $4 trillion company?
NVIDIA became the first-ever $4 trillion public company on July 10, 2025, driven by surging demand for AI infrastructure, particularly its GPUs powering generative AI platforms like ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini. Their stock has soared—up ~15× since late 2022 and ~22% in 2025 alone—as major tech firms race to build AI data centers using NVIDIA hardware . With revenues topping $44 billion in Q1 (+69% YoY) and 95% market share in AI-focused GPUs, NVIDIA has cemented its position as the essential “picks and shovels” of the AI gold rush.
Could Nvidia become a 10 trillion dollar company?
Yes, Nvidia could potentially reach a $10 trillion valuation if global demand for AI infrastructure, GPUs, and data centers continues to surge. Sustained innovation, dominance in AI chips, and expanding use of generative AI could drive future growth—though reaching $10 trillion would require strong execution and favorable market conditions.
Why is Nvidia becoming so rich?
Nvidia is becoming extremely rich due to its dominance in AI chips and GPUs, which power technologies like ChatGPT, autonomous vehicles, and data centers. As demand for generative AI soars, major tech companies rely on Nvidia’s hardware, driving massive revenue growth, high profit margins, and a skyrocketing market valuation.
What made Nvidia so successful?
Nvidia’s success stems from its early leadership in GPU technology and smart pivot to AI and data center computing. Its chips power advanced AI models, making it essential to companies like OpenAI and Google. Strategic innovation, strong partnerships, and dominance in the AI hardware market fueled its rapid rise.
Does Apple use Nvidia chips?
Apple does not use Nvidia GPUs in its AI infrastructure. Instead, Apple relies on Google’s TPUs—specifically the TPUv5p and TPUv4 models—to train its AI models . Additionally, Apple does not purchase Nvidia hardware for on-premise use but may rent Nvidia GPUs via providers like Amazon and Microsoft. They’re also developing their own AI chips (codenamed Baltra, with Broadcom) aiming for mass production by 2026, to further reduce dependence on external vendors.








