A 3D printer typically uses 50 to 150 watts of electricity on average. This consumption is similar to that of a desktop computer.
Understanding the power requirements of a 3D printer is crucial for enthusiasts and professionals alike. Electricity consumption can vary based on the size of the printer, the temperature of the heated bed, and the printing material used. Home-based 3D printers generally consume less power compared to industrial models.
This relatively modest electricity usage makes 3D printing a cost-effective technology for rapid prototyping and small-scale manufacturing. Users should consider these operational costs when planning their 3D printing projects. Keeping energy consumption in mind also helps in making environmentally conscious decisions while enjoying the innovation 3D printing brings to various industries.

The Basics of 3D Printer Electricity Consumption
Understanding your 3D printer’s energy use is crucial. Like any other appliance, a 3D printer draws electricity to operate. But just how much does it consume? Factors like printer size, type, and print duration impact power usage. In this section, we’ll delve into what affects a 3D printer’s electricity consumption and how to measure it effectively. This knowledge helps control your energy bills and ensures efficient printer operation.
Factors Influencing Power Usage
Several aspects determine a 3D printer’s power consumption:
- Printer size: Larger printers often draw more power.
- Print speed: Higher speeds may lead to increased energy use.
- Temperature settings: Higher extrusion and bed temperatures can up the energy needed.
- Material type: Materials like ABS require more energy to print than PLA.
- Model complexity: Complex prints with longer durations use more electricity.
Keep these factors in mind as they play a significant role in how much energy your 3D printer consumes during its operation.
Measuring 3D Printer Energy Consumption
Tracking your printer’s energy use is simple with the right tools. A common method is using an electricity usage monitor. You just plug your printer into the monitor, and it displays the power consumption. By keeping an eye on usage, you can adjust settings or practices to save on energy without compromising print quality.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Connect the 3D printer to the energy monitor. |
| 2 | Start your print job as usual. |
| 3 | Monitor the energy usage display. |
| 4 | Record the consumption data for analysis. |
By measuring and understanding your 3D printer’s electricity use, you can make better decisions on how to print efficiently. This not only reduces energy costs but also minimizes your environmental footprint.
The Costs of 3D Printing
3D printing revolutionizes the way we create objects, from toys to tools. Yet, many overlook its electricity consumption. Let’s unfold the costs of 3D printing to better understand its impact on your bills.
Calculating Electricity Costs For 3D Printing
3D printers vary in power usage, which affects the cost. To calculate the cost, consider these factors:
- Printer Wattage: Check the printer’s specifications for power consumption.
- Printing Time: Longer prints use more electricity.
- Electricity Rate: Find this on your utility bill, measured in cents per kilowatt-hour.
Use the formula: Printer Wattage (kW) x Printing Time (hours) x Electricity Rate ($/kWh) to estimate costs.
Tip: To save on costs, use a printer with Energy Star certification.
Cost Comparison With Traditional Manufacturing Methods
3D printing often stands out for its lower setup costs compared to traditional methods like injection molding. Yet, each has different energy needs.
- Energy Efficiency: 3D printers typically use less energy, cutting costs.
- Waste: Traditional methods may waste materials, whereas 3D printing is more precise.
- Volume: In high-volume production, traditional methods might be more cost-effective despite higher initial costs.
For small-scale production, 3D printing can lead to significant savings on energy expenses.
Remember, energy use is just one factor. Material costs, labor, and equipment maintenance also contribute to the overall costs of manufacturing.
How Much Does It Cost to 3D Print for One Hour?
To determine the cost of 3D printing per hour, you need to account for several factors:
- Electricity Costs: Based on the power consumption of your 3D printer.
- Material Expenses: The cost of filament or resin used.
- Labor Charges: Time spent monitoring or setting up the printer.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular upkeep and repairs.
- Additional Costs: Items like support materials or specialized equipment.
By considering these components, you can calculate a detailed estimate for the hourly cost of 3D printing. A simplified formula to help with this calculation is:
Total cost per hour = Electricity* + Material costs* + Wear and tear + Labor costs + Amortized printer costs + Overheads
Electricity Cost = (Printer Power Consumption in KW) x (Printing Hours) x (Electricity Rate per kWh)
Material Cost = (Material Price per Unit) x (Material Consumption per Hour)
Energy-efficiency In 3D Printing
Knowing the electricity consumption of a 3D printer allows us to make more eco-friendly choices. 3D printers vary in their energy consumption based on size, type, and complexity. They can use as little energy as a laptop or much more. Energy efficiency is becoming a key feature in 3D printing. This is to save costs and reduce environmental impact.
Tips For Reducing Electricity Usage
Save energy and money with these simple steps:
- Print Smarter: Plan prints to lower waste and time.
- Energy-Saving Modes: Use them when available.
- Optimizing Print Speed: Find a balance between speed and energy use.
- Maintenance: Keep your printer in top shape to save energy.
Innovations In Energy-efficient 3d Printers
New 3D printers come with cool features for energy saving:
- Low-Power Modes: They limit energy use when the printer is idle.
- Efficient Components: Parts that use less power.
- Energy Monitoring: Track and manage power usage.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Eco-Friendly Materials: | Less energy to print. |
| Software Optimization: | Reduces unnecessary energy use. |
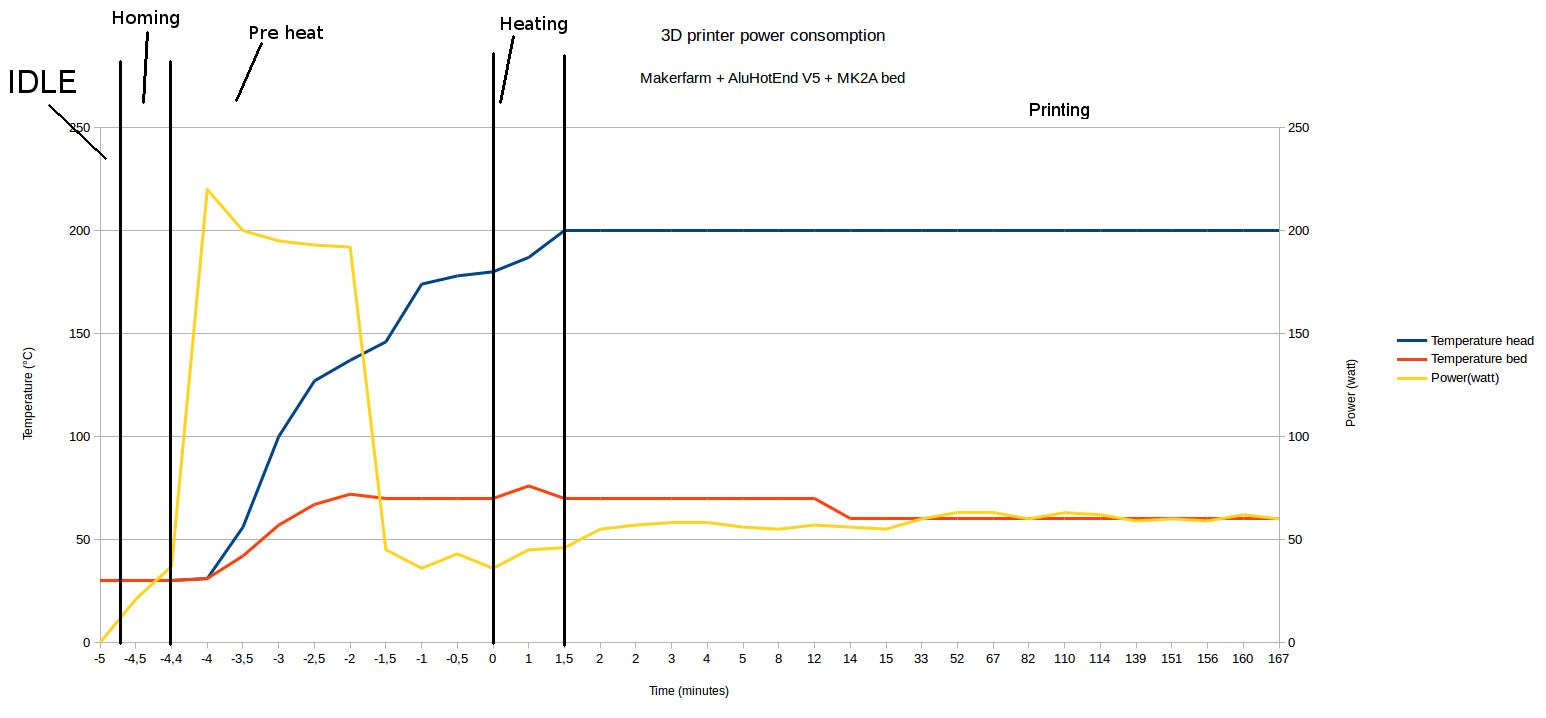
Real-world Examples
Welcome to the ‘Real-World Examples’ segment. Here, we delve into how 3D printers perform in actual scenarios. Users wonder about the power consumption of these innovative machines. Let’s look at some case studies and industry practices.
Case Studies Of Electricity Use In 3D Printing
A real-life study helps us understand energy usage. For instance, consider a desktop 3D printer model. It uses about 50 watts during printing. But this may change with the printer size and complexity. A study by Michigan Technological University revealed varied results. It highlighted that some printers consume up to 100 watts. Another study showcased that industrial printers often use more than 1000 watts. Such insights help users to gauge power cost in 3D printing.
Industry Best Practices For Energy Management
The 3D printing industry is not just about creativity. It also focuses on energy efficiency. Many companies employ strategies to cut down electricity use. They optimize print settings and use energy-efficient models. Some best practices include:
- Timed Printing: They plan print jobs for low-demand energy hours.
- Maintenance: Regular check-ups ensure machines work efficiently.
- Software: Advanced software predicts energy requirements.
Companies keep track of usage through monitoring systems. This helps in managing costs and eco-footprints.
Which 3D Printers Offer Cost-Effective Printing?
When looking for cost-effective 3D printers, it’s important to consider factors like initial cost, material compatibility, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Here are some budget-friendly options known for their affordability and performance:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Printers
- Creality Ender 3 Series (Ender 3, Ender 3 Pro, Ender 3 V2)
- Price: $200–$300
- Features: Open-source design, easy upgrades, and wide material compatibility.
- Why It’s Cost-Effective: Affordable initial cost and low material expenses.
- Prusa Mini+
- Price: ~$400
- Features: Compact size, automatic bed leveling, and high-quality components.
- Why It’s Cost-Effective: Excellent print quality with minimal maintenance.
- Anycubic i3 Mega S
- Price: ~$300
- Features: Sturdy frame, touchscreen interface, and filament sensor.
- Why It’s Cost-Effective: Reliable and easy to use with minimal setup.
- Artillery Sidewinder X2
- Price: ~$450
- Features: Large build volume, direct drive extruder, and quiet operation.
- Why It’s Cost-Effective: Ideal for larger prints with consistent performance.
Resin Printers
- Elegoo Mars 3
- Price: ~$300
- Features: 4K monochrome LCD, high-resolution printing, and user-friendly interface.
- Why It’s Cost-Effective: Delivers exceptional detail at a competitive price.
- Anycubic Photon Mono X
- Price: ~$500
- Features: Large build volume, fast curing times, and 4K resolution.
- Why It’s Cost-Effective: Suitable for professional-quality prints at a reasonable cost.
- Creality Halot-One
- Price: ~$250
- Features: Compact design, Wi-Fi connectivity, and detailed printing.
- Why It’s Cost-Effective: Affordable entry point into resin printing.
Other Considerations
- Material Compatibility: Choose printers compatible with cost-effective filaments or resins (e.g., PLA or standard resin).
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for models with lower power consumption.
- Support and Upgrades: Brands like Prusa and Creality offer extensive community support and upgrade paths, making them long-term investments.
By balancing initial costs, material expenses, and operational efficiency, these models provide excellent value for 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do 3D Printers Make Electric Bill Go Up?
3D printers can increase your electricity bill slightly due to their power usage during printing operations. The impact varies based on printer efficiency and usage frequency.
How Much Does It Cost To Run A 3D Printer Per Hour?
The cost to run a 3D printer per hour typically ranges from $0. 05 to $0. 50, depending on the printer’s power consumption and electricity rates.
How Much Electricity Does A Ender 3 3D Printer Use?
An Ender 3 3D printer uses approximately 100 watts of electricity during printing. On standby, it consumes about 18 watts.
How Do You Calculate The Cost Of Electricity For A 3D Printer?
To calculate the cost of electricity for a 3D printer:1. Multiply the printer’s wattage by hours of use. 2. Multiply this number by your electricity rate per kWh. 3. Convert the result to your currency for the total cost.
Is a 3D printing business profitable?
A 3D printing business can be profitable, especially when focused on high-demand niches like prototyping, custom products, medical models, or education. Success depends on managing costs, such as affordable materials and energy-efficient printers, and offering unique, high-quality services.
While competition and skill requirements pose challenges, businesses can thrive by targeting specific markets, pricing strategically, and scaling operations efficiently. Examples of profitability include custom product manufacturing, B2B prototyping, and selling design files or services online. Careful planning and market research are essential to maximize profitability in this dynamic industry.
In Summary
Monitoring your 3D printer’s electricity consumption is crucial for controlling costs and optimizing energy use. It varies based on model, use frequency, and complexity of prints. Remember, regular maintenance can also help in keeping efficiency high. Stay savvy with your 3D printing adventures and mindful of the electricity you use!